Our customers are very satisfied with the quality and delivery time.
GL9693 (-)-Nicotine hydrogen tartrate salt
(−)-1-Methyl-2-(3-pyridyl)pyrrolidine (+)-bitartrate salt; Nicotine bitartrate dihydrate; Nicotine ditartrate dihydrate; Nicotine powder; Nicotine tartrate
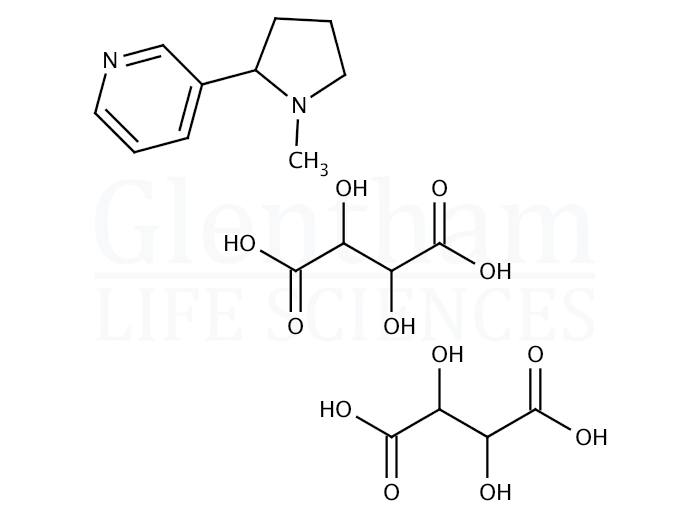

(-)-Nicotine hydrogen tartrate salt
$55.50
🟢 In Stock (5+)
Product code: GL9693-1g
Packaging type: glass vial (packaging info)
Description: 5ml amber glass vial with 18mm neck + blue cap with PTFE wad
Material: Amber glass
Dimensions: 22 x 22 x 48 (mm)
Volume: 5 (ml)
UN certified: No
Weight: 20.182
Size
1g
5g
bulk
Dispatches: 16th April 2024
Note: Please contact us if you require ISO 13276 purity testing for this material
Product Description
Nicotine is a naturally derived alkaloid found in the nightshade family of plants. It is a toxic, highly addictive central nervous system stimulant. Nicotine hydrogen tartrate salt is more stable during storage than the base form.
| Glentham Code | GL9693 |
| Product Categories | APIs, Biochemicals, Phytochemicals, Alkaloids |
| CAS RN | 65-31-6 |
| Alternative CAS RN | 6019-06-3 (·2H2O), 2624-48-8, 54-11-5 (base) |
| EC Number | 200-607-2 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00069368 |
| Storage Temperature | +4°C |
| Shipping Temperature | Ambient |
| Harmonised Tariff Code | 2939791000 |
| Regulatory information | This product is subject to regulatory requirements that must be followed after purchase |
Top Reviews
Our happy customers
Excellent range of chemicals and… Excellent range of chemicals and buffers combined with great service and pricing.
Glentham lifescience. product is very good.And the quality is also very good.We are very happy with your local distributor in Pakistan.And your local distributor is doing a great job.
Very good! Thanks, Nicholas and Sam!
"Excellent products and amazing lead times."
Excellent products and amazing lead times. A definitive for any lab
Impressive experience with Glentham Life Sciences Great products, Fast shipping, Nice support, Reliable partner
Good experience . 100% Product Purification with Better Result very cooperative staff and excellent dealings with distributors
Glentham is the best company. It is a company that strives with each other for the development of the Glentham and distributor. It's a great company that provides quality products at a good price.
High quality products and good support.
Excellent We have been working with Glentham Life Science since 2012. Most of the End- used comments evaluate high quality chemicals.
Our customers are very satisfied with the quality and delivery time.
Successful market for Glantham in Qatar My experience with Glenthan Life Sciences is an excellent company with respect to quick reply to the customers and providing high-quality chemicals and fine chemicals. Many times we get the invoices and we make the payments and we receive the items within one week, a process that makes our customers so happy with the service particularly we are ba…
A great company to work with! We have been working with Glentham since 2017 and they supply a large percentage of our raw materials. During that time both they and we have seen large growth, but we still find they have managed to retain the personal touch that we value so much. Always helpful and ready to seek out some unusual requests, Glentham also maintain very competitive prices which…
Great chemicals supplier. Many items in stock , all with high quality.
You science and research partner! We've been working with Glentham from years now. They are very trustful, helpful solving issues and always reliable. The Customer service is always ready and very kind. Absolutely a good company to work with.
Trustworthy and reliable supply partner… Trustworthy and reliable supply partner for quality raw materials and research needs...Keep it up!!
Excellent products Excellent products, great lead times and a very helpful support team
We have always had a very positive experience of working with Glentham Life Sciences. Their customer service is excellent and their stock levels & lead times are very impressive, which is important to our business and we will certainly continue to buy from them as a result
The best company I have ever worked with.
A pleasure to deal with, high quality products and a very good supply chain with speedy delivery times
Research chemicals are good quality,lead time excilent & many items are ready stock
Great service Great service! Good prices and wide range of products.
Glentham Life Sciences products is very good quality and quickly response him
Glentham life sciences very high quality products company
Good experience.very cooperative staff ,good items and excellent dealings with distributors.
Got a question for us?
Please fill in the enquiry form to contact our customer service, for technical support, or for any requests. We will get back to you as soon as possible.



